Lymphoedema


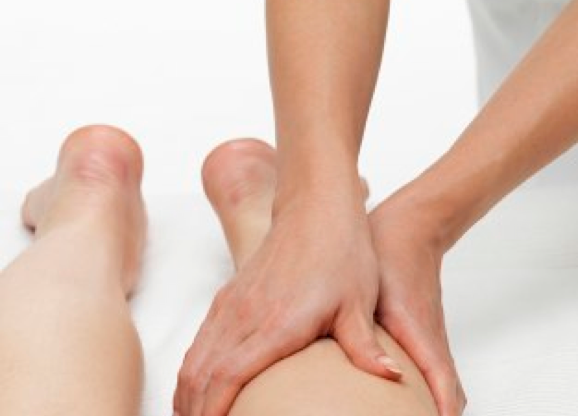
Lymphoedema is a condition that results in progressive swelling of a limb because the lymphatic circulation fails to transport fluid via the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes.
Traditionally lymphoedema has been classified into primary and secondary:-
Primary lymphoedema mainly occurs as a result of poor development or absence of the lymphatic system and can be hereditary. Secondary lymphoedema occurs when the lymphatic channels become blocked because of infection, following surgery, radiotherapy or as result of an obstructing lesion.
Although the diagnosis of lymphoedema can usually be made following examination of the patient a number of tests are available to verify or classify the condition. These include, lymphangioscintigraphy, CT scan, MRI scan and contrast lymphangiography.
Treatment will have to be tailored according to the cause and severity of the condition. The basic principle however is to reduce limb swelling. This can be achieved by using simple measures such as elevating the limb, compression hosiery, physiotherapy and manual lymphatic drainage. In the extreme cases debulking surgery may be required. Another important principle is minimising the risk of infection to the affected limb and prompt antibiotic therapy if infection occurs.
Previous: Diabetic Foot
Next: Lipodema
Lymphoedema