Thoracic Outlet Syndrome


Thoracic Outlet Syndrome




















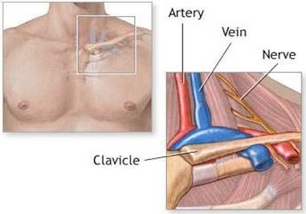
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is a condition which involves the nerves, arteries and veins supplying an arm. It is a relatively under-diagnosed condition and often affects otherwise well individuals. It occurs when the blood vessels and nerves are compressed as they pass through a tight space between the collar bone (clavicle), ribs and fibrous tissues. Some patients have an extra rib above the 1st rib which causes the compression, but the majority have compression due to the 1st rib.
Compression of the nerves can lead to muscular wasting of the hand and altered sensation. Arterial compression can lead to cold hands, pallor or a bluish tinge in the affected limb and cramping in the muscles of the arm when being used. Compression of the vein can often cause a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the affected limb which leads to pain and swelling. This is commonly a presenting symptom.
A special MRI scan can be performed to identify the cause and location of the compression.
Physiotherapy can often help to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint and reduce the symptoms of nerve compression. If there is a DVT from venous compression, blood thinning medication will be started. Surgical intervention in the form of a 1st rib resection may be performed where there are symptoms related to the blood supply. It involves making an incision in the armpit and removing part of the 1st rib and some of the surrounding tissue. If there is a significant narrowing of the vein or artery, an angioplasty or venoplasty may be performed in order to use a balloon to open up the blood vessel. Alternatively, an open operation can be performed in the neck to widen the blood vessels, known as patch angioplasty.
Previous: Arteriovenous Malformations
Next: Hyperhidrosis