Peripheral Vascular Disease


time when lying down. If this persists or the blood vessel gets blocked completely, ulceration and gangrene can occur in the foot and the lower leg.
Blood pressure measurements in the leg, known as ankle-brachial pressure indices (ABPI), can be used to indicate the severity of narrowing. Arterial duplex ultrasound scans can be used to image and monitor the narrowing in the leg arteries in a similar manner to carotid doppler scans. In the majority of cases a CT angiogram may is performed to obtain more detailed images.
Treatment can be both non-operative and operative. All patients should be started on lipid lowering drugs, known as Statins, which have been shown to stabilise the plaque. Low dose aspirin is also prescribed to reduce the risk of clots forming. Raised blood pressure and diabetes should be treated appropriately and smokers should be encouraged to stop as quickly as possible.
Peripheral Vascular Disease





















Angioplasty - This animation shows a (drug eluting) balloon angioplasty technique being used to treat a narrowed segment of an artery.
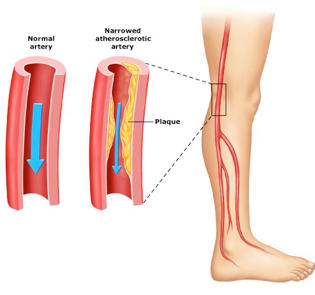
Similar to the plaque build up, which causes coronary artery (heart) and carotid artery disease, there can also be plaque in the arteries of the legs. Narrowing of the blood vessel typically causes cramping in the calf or buttock muscles of the affected leg when walking. After resting for a few minutes, the cramping pain stops and the patient is able to walk again. This is known as intermittent claudication.
If the narrowing becomes very severe, patients will often find that they have pain in the foot at night
In patients who have mild to moderate disease, exercise in conjunction with the measures described above, have been found to have good effect. Medication such as Naftidrofuryl Oxalate (Praxilene®) can be prescribed to help improve the walking distance giving a better quality of life.
Patients who have severe disease will often require operative intervention. A large proportion of these patients will be suitable for a minimally invasive procedure known as angioplasty. This involves using a balloon to open up the narrowing in the affected blood vessel and sometimes placing a stent. This a pinhole operation and the patient can usually go home the same day.
With the newer angioplasty techniques such as sub-intimal recanalisation and the ‘’safari’ technique’’ we could treat endovascularly even extensive disease that in the past could only be treated with open surgery.
Previous: Aortic Dissections
Next: Diabetic Foot